Did You Know?!
In the European Union each year, an estimated 2,000 children (14 years or younger) choke on a toy.[Ref:34]
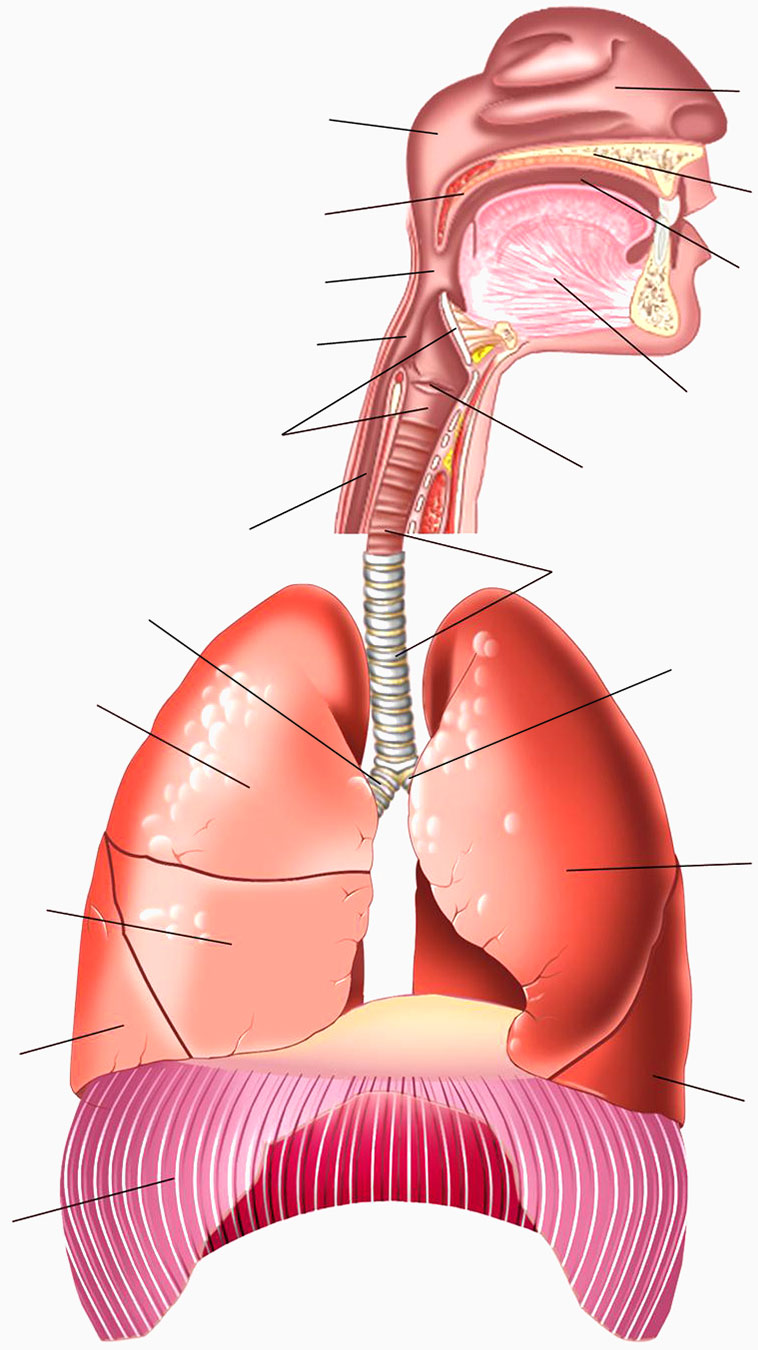
The safety of our upper aerodigestive tract revolves around on the function of our larynx.
To see images of anatomical areas with foreign bodies, see Partial Obstruction or Extraction Cases.
The nasal cavity refers to the two air spaces (on either side of the nasal septum) which extend from the front of the nose to the nasopharynx. The nasal cavity filters and humidifies air. In teens and adults, the nasal cavity is about 5 cm long. Toddlers often put objects into their nasal cavities, but usually this does not lead to choking.
The first section of the roof of the mouth, located in front of the soft palate. The hard palate contains bone.
The oral cavity lies behind the teeth and in front of the oropharynx. The oral cavity contains most of the tongue.
The tongue is the muscular organ in the oral cavity, used for tasting, licking, swallowing, and articulating speech.
The true vocal cords are two white ligaments within the larynx (just below the pink false vocal cords). By opening and closing, our vocal cords help us breathe, talk and swallow safely. Please see The Amazing Larynx page for more info.
The trachea, also called the windpipe, is the breathing tube that connects the larynx to the bronchi. Firm arches (made of cartilage) prevent the trachea from collapsing.
The lungs are a pair of breathing organs, located within the chest, which facilitate the exchange of carbon dioxide for oxygen in our blood. The right lung has three lobes; the left lung has two lobes.
The lungs are a pair of breathing organs, located within the chest, which facilitate the exchange of carbon dioxide for oxygen in our blood. The right lung has three lobes; the left lung has two lobes.
The muscle that separates the chest (thoracic) cavity from the abdomen. The diaphragm is the main muscle of respiration. Contraction of the diaphragm muscle allows the lungs to expand during inspiration (when air is inhaled).
The lungs are a pair of breathing organs, located within the chest, which facilitate the exchange of carbon dioxide for oxygen in our blood. The right lung has three lobes; the left lung has two lobes.
The lungs are a pair of breathing organs, located within the chest, which facilitate the exchange of carbon dioxide for oxygen in our blood. The right lung has three lobes; the left lung has two lobes.
The lungs are a pair of breathing organs, located within the chest, which facilitate the exchange of carbon dioxide for oxygen in our blood. The right lung has three lobes; the left lung has two lobes.
The larynx, also known as the voicebox, contains our vocal cords. The epiglottis is the shield-like structure above the vocal cords. The epiglottis helps divert food and drink to each side of the larynx (into the hypopharynx). The epiglottis usually does not cover the larynx.
The soft palate is the fleshy, flexible part towards the back of the roof of the mouth.
The esophagus is the elastic swallowing tube in your chest; it connects the hypopharynx to the stomach and stretches as food slides down it.
The upper part of the pharynx, connecting with the nasal cavity (above the soft palate).
The area of the throat that lies behind the oral cavity (between the nasopharynx and the hypopharynx). The oropharynx contains your tonsils and uvula (at the end of the soft palate, in the middle).
The hypopharynx is the lowest portion of the pharynx, extending from the base of the tongue to the esophageal inlet.
The Right Main Bronchus connects the trachea to smaller bronchi, which branch out towards the 3 lobes of the right lung.
The Left Main Bronchus connects the trachea to smaller bronchi, which branch out towards the 2 lobes of the left lung.
In the European Union each year, an estimated 2,000 children (14 years or younger) choke on a toy.[Ref:34]